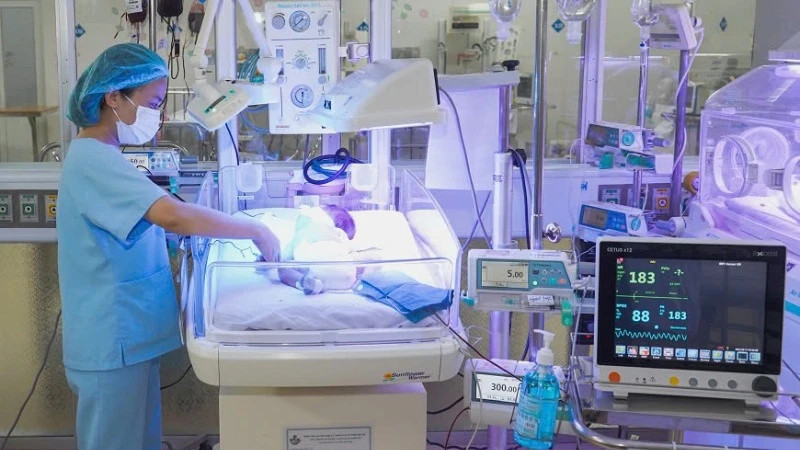
The health facility network planning issued by the Prime Minister is built in accordance with the orientation and vision of national development, the socio-economic development strategy, the national master plan and other relevant national-level plans.
It aims to develop a network of health facilities to ensure the provision of comprehensive, integrated and continuous services so that all people have convenient access to health protection, care and improvement services at reasonable costs, in order to improve both physical and mental health, stature, longevity and quality of life of Vietnamese people; ensuring health security, timely response to climate change and emergency situations.
On the other hand, attention will be paid to develop a network of health facilities to ensure balance, synchronisation, connectivity and efficiency between the national health facility network and the local health facility network, on the basis of applying science and technology and digital transformation, in line with the international integration trend.
It also aims to develop a network of health facilities in the direction of harmoniously combining grassroots health care and specialised health care; between traditional medicine and modern medicine; between armed forces health care and civilian health care associated with building the potential of national defense and security health care; ensuring the provision of health services to disadvantaged areas, gradually narrowing the development gap between regions, areas, and areas, towards the goal of all people having access to quality health care services.
Associate Professor, Dr. Phan Le Thu Hang, Deputy Director of the Department of Financial Planning under the Ministry of Health said developing a network of health facilities in the direction of fairness, efficiency, development and international integration is carried out through the development of technical expertise at the intensive care level (in which some hospitals are developed into modern, high-tech intensive hospitals, on par with developed countries in the region and internationally); increasing the total supply of end-line intensive care services, including both the total supply and end-line intensive service supply of a number of priority specialties such as oncology, cardiology, obstetrics/obstetrics - pediatrics, geriatrics, rehabilitation, traditional medicine, infectious diseases; improve the geographical distribution of hospitals providing end-line intensive care services to improve geographical accessibility (upgrade some general hospitals, provincial specialised hospitals to assume regional functions, develop satellite network of central hospitals, build new central hospitals in the Central Highlands, Mekong Delta...)
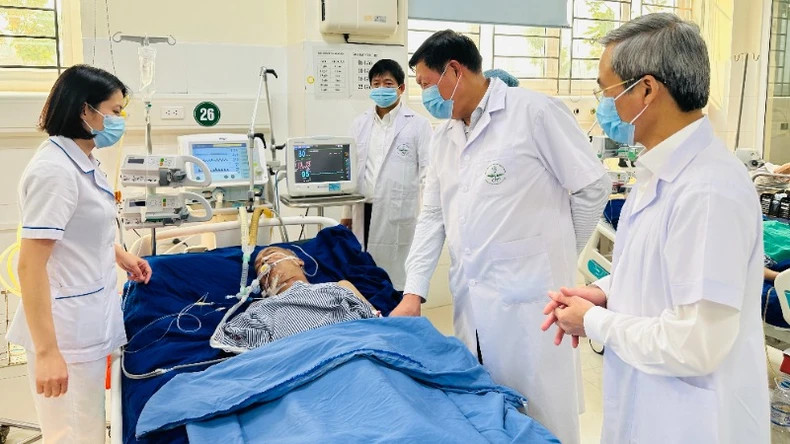 |
| Son La Provincial General Hospital continuously improves quality to meet the health care needs of local people. |
Regarding the long-term orientation, the Health Facility Network Planning mentioned the formation of two specialised medical complexes when conditions are sufficient in the North and South. Medical complexes are considered by many experts to be a model that can help create a boost for innovation and high-tech development activities of the entire health sector, in line with the goal of creating a modern, advanced health system as well as the view that health is a service industry capable of directly contributing to economic growth.
Medical complexes are considered most suitable for health facilities with large and complex laboratory systems; high-tech biomedical research and development centres; large health human resource training facilities; high-tech medical examination and treatment facilities (hospitals and clinics); facilities for research and production of pharmaceuticals, biological products and high-tech medical equipment, etc.
This model brings many advantages including creating space for cooperation and sharing of shared medical technical infrastructure between health facilities, especially between lab systems; creating a space for linking research, development, human resource training and design and production of high-tech pharmaceutical products; facilitating investment and operation of some common technical infrastructure items for facilities in the complex; facilitating the design of key investment projects (requiring large-scale concentrated investment capital); and partly facilitating investment preparation because it is only necessary to secure the site once at one location, instead of having to solve the problem of securing the site multiple times at many different locations.
Analyzing the capacity of the health system after 2030, experts in the health sector noted that the synchronous implementation of policy solutions on innovation in the method of providing health services towards focusing on primary health care, health promotion, disease prevention as well as solutions to improve the quality of health services; developing health human resources; innovating health financing mechanisms will improve the response capacity of the Vietnamese health system.
People will mainly use health services at the grassroots level and then the need to use health services at the end of the line will mainly focus on specialised health services. Therefore, after 2030, it is necessary to focus on developing and expanding more specialised medical centers (oncology, cardiology, geriatrics, endocrinology, psychiatry) associated with the general hospital system as well as developing a system of specialised hospitals in a number of priority areas such as oncology, cardiology, geriatrics to meet the changes in disease patterns in the years after 2030.
To realise that goal, the Plan determined to mobilise and effectively use investment capital from state budget sources; official development assistance (ODA) capital and preferential loans, non-refundable aid not included in official development assistance from foreign agencies, organisations and individuals for Vietnam; funds for developing career activities of medical facilities; private investment sources; other legal funding sources.
On the other hand, it is expected to effectively use public investment to activate, mobilise, and attract all social resources, especially private resources, to participate in investment projects to develop health facilities according to the plan; prioritise public investment in infrastructure development for health facility networks in areas with difficult economic conditions, remote areas, border areas, seas, islands, and areas with limited revenue sources.