According to statistics from the Ministry of Health, in 2025 Viet Nam recorded more than 3,000 food safety violations, with over 30% involving food of unclear origin or without safety certification. Most cases occurred during peak consumption periods such as Tet.
The Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) said it has been actively promoting the rollout of QR codes and product traceability tools to protect public health. Beyond reducing risks from counterfeit and substandard food, the technology is also bringing noticeable changes for both consumers and businesses.
Reliable consumption thanks to technology
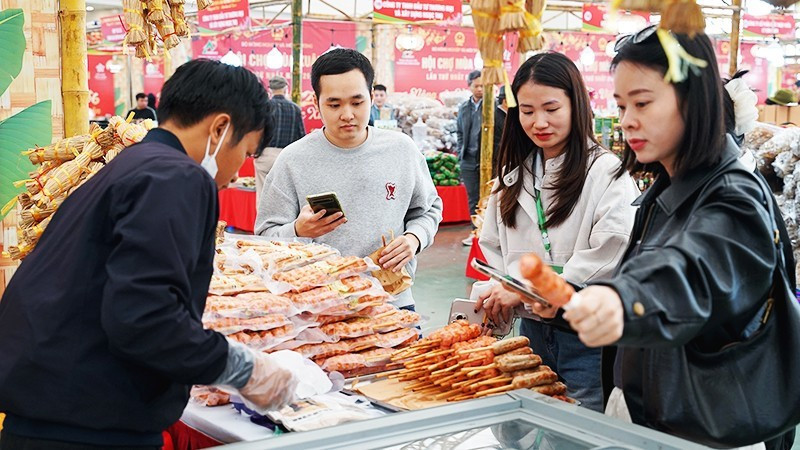
Poor-quality food, counterfeits and imitation goods remain persistent problems that consumers face every day. To address this, MOST has moved to deploy modern management tools such as QR codes, electronic labels and a national quality monitoring system. QR codes — capable of providing fast and accurate traceability information —are seen as an effective tool to reduce the risk of counterfeit products and unsafe food.
Ngo Thu Lan (35 years old), a consumer in Cua Nam Ward (Ha Noi City), previously had the habit of buying food at traditional markets. In her view, shopping at markets is convenient and often cheaper than supermarkets or shops. However, because the origin of goods cannot be controlled, she has long worried about quality and potential safety risks.
Faced with increasingly serious food safety violations in recent times, Lan decided to change her habits, prioritising purchases from shops or supermarkets where product origins can be verified via QR codes.
“Before QR codes were printed on product packaging, I was very worried about food quality, especially during Tet. When buying gio cha or sweets, I only dared to buy familiar brands. But since these products started carrying QR codes, I just scan the code and can immediately see the origin of the product and how it was made. That gives me much greater peace of mind,” Lan said.
With a simple action on a phone, users scan the QR code on the packaging. The code leads to a website that provides detailed information on processing, the manufacturer’s food safety certifications, and even videos demonstrating the production process. “I feel more confident when I know the product I buy has been tested and meets quality standards,” Lan added.
Thanks to these features, many consumers have changed their food-buying habits — from choosing only familiar products to seeking items that are transparent about origin and production processes.
Alongside consumers, businesses are also actively adopting QR codes to improve product quality and protect their brands. Hoa Binh Enterprise, which specialises in ready-to-eat processed foods, is a typical example of applying technology to product management.
According to Nguyen Van Hoa, Director of Hoa Binh Food Production Company, applying QR codes helped the company increase revenue by up to 25% in 2025.
Nguyen Van Hoa, Director of Hoa Binh Food Production Company in Duy Tan Ward, Ninh Binh Province, said that since 2025 the company has invested in designing a complete QR code system for its products. With the firm’s core products being processed foods, consumers have an even stronger need to understand origins in order to ensure safety.
“Previously, without QR codes, we could only protect our brand through food safety certifications. But since adopting QR codes, consumers can instantly trace all product information with a single scan. This not only helps us demonstrate product quality but also builds strong trust among customers,” Hoa said.
From selling specific products, the company is gradually shifting towards selling trust. Hoa also believes technology does not only help businesses grow; it also contributes to a healthier competitive environment in the food sector. When his company’s products can be inspected and traced easily, other businesses are compelled to improve quality and disclose information, thereby raising fair competition in the processed food industry.
Protecting consumers, helping to make the market transparent
A representative of MOST, Tran Hau Ngoc, Vice Chairman of the National Metrology, Standards and Quality Committee, said: “We have implemented a number of strong solutions to respond to counterfeits and unsafe food, especially during the Lunar New Year. One of the key tools in food safety management is the use of modern technologies such as QR codes and product traceability systems.”
According to Ngoc, since 2025, MOST has worked with relevant authorities to conduct tighter inspections and monitoring of food origins through traceability systems, with QR codes playing a central role. Recently, MOST also launched a project to build a product quality monitoring system, under which food products will be labelled with QR codes to enable easy checks of production processes, product quality and food safety certifications.
“Applying QR codes enables consumers to verify product origins easily, while also allowing us to monitor closely and detect substandard goods, counterfeits and unsafe food early. This technology strengthens transparency and protects consumer rights,” Ngoc stressed.
Despite clear benefits, applying QR codes to food safety control still faces several challenges.
First, not every business has the capability or finances to implement a full QR code system. Small and medium-sized enterprises still struggle with investing in technology and maintaining such systems.
Second, some consumers are not yet accustomed to using technology to check products, particularly middle-aged and older groups. Limited familiarity with smartphones and scanning QR codes is also a factor that reduces the effectiveness of the approach.
However, MOST said it has plans to address these limitations, including supporting small and medium-sized enterprises in adopting new technology and running awareness campaigns to inform the public of the benefits of using QR codes to ensure food safety.
Applying QR codes to food safety control is an important step towards improving food governance in Viet Nam. Although challenges remain, real-life stories from consumers and businesses show that technology can play a major role in creating a more transparent and safer food market. In particular, amid strong digital transformation, applying technology is not only a trend but an urgent requirement to protect public health and support the sustainable development of the food industry.